virtualThread
jdk21, spring boot 3.2 버전부터 virtualThread가 도입되면서 한동안 크게 변치 않던 java의 thread 처리방식에 변화가 생겼습니다. 기존 플랫폼 스레드를 사용할때의 단점을 보완하여 멀티쓰레드 프로그램의 처리량을 더 늘리기 위한 목적으로 신규 도입된 기능입니다.
virtualThread 관련한 설명은 아래 포스팅에서 아주 자세히 잘 다루고 있으니, 이 포스팅에서는 설명을 생략하고 예제 코드를 통해서 virtualThread를 통해 실제 성능개선이 어느정도 일어나는지 확인해보도록 하겠습니다.
- https://d2.naver.com/helloworld/1203723
code for test
virtualThread의 성능 개선 여부는 CPU 바운드 작업 혹은 IO 바운드 작업인지에 따라서 결과가 달라질 수 있습니다. 이를 테스트 하기위해 간단하게 multiThread 호출 성능을 비교하는 2개의 Thread Executor를 세팅해보도록 하겠습니다.
// async configuration
@EnableAsync
@Configuration
public class AsyncConfig {
@Bean(name = "threadPoolTaskExecutor")
public Executor threadPoolTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(50);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(100);
executor.setQueueCapacity(1000);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("Async-Thread-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Bean(name = "virtualThreadPoolTaskExecutor")
public Executor virtualThreadPoolTaskExecutor() {
SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor executor = new SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor();
executor.setVirtualThreads(true);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("V-Thread-");
return executor;
}
}
// controller
@RestController
public class AsyncExampleController {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncExampleController.class);
@Autowired
private AsyncExampleService asyncExampleService;
@GetMapping("/run/cpu")
public void runCpuExample() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 1000개의 비동기 작업 실행
List<CompletableFuture<String>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
futures.add(asyncExampleService.executeCpuTask(i));
}
// 모든 작업이 완료될 때까지 대기
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])).join();
stopWatch.stop();
log.info("All tasks finished in {} ms", stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis());
}
@GetMapping("/run/io")
public void runIoExample() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 1000개의 비동기 작업 실행
List<CompletableFuture<String>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
futures.add(asyncExampleService.executeIoTask(i));
}
// 모든 작업이 완료될 때까지 대기
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])).join();
stopWatch.stop();
log.info("All tasks finished in {} ms", stopWatch.getTotalTimeMillis());
}
}
// service
@Slf4j
@Service
public class AsyncExampleService {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AsyncExampleService.class);
// @Async("threadPoolTaskExecutor")
@Async("virtualThreadPoolTaskExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> executeCpuTask(int taskId) {
log.info("Task {} : start", taskId);
calculatePrimes(1, 1000000);
log.info("Task {} : completed", taskId);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("Task " + taskId + " finished");
}
// 주어진 범위 내에서 소수 개수 계산
private int calculatePrimes(int start, int end) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++) {
if (isPrime(i)) {
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
// 소수 판별 함수
private boolean isPrime(int number) {
if (number <= 1) return false;
for (int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(number); i++) {
if (number % i == 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
// @Async("threadPoolTaskExecutor")
@Async("virtualThreadPoolTaskExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> executeIoTask(int taskId) {
log.info("Task {} : start", taskId);
long result = readFile();
log.info("Task {} : completed ({})", taskId, result);
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture("Task " + taskId + " finished");
}
private long readFile(){
long sum = 0;
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource("sample/exampleTest.txt");
try(BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(resource.getInputStream()))){
String s = "";
while((s = br.readLine()) != null){
String countStr = StringUtils.split(s, "exampleTest-")[1];
sum += Long.valueOf(countStr);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return sum;
}
}
threadPoolTaskExecutor: platform 스레드 사용virtualThreadPoolTaskExecutor: virtual 스레드 사용
CPU 바운드 작업의 경우 소수판별 로직을 넣어 적용했고, IO 바운드 작업은 resource 파일 read 작업을 넣어 테스트코드를 구현했습니다.
결과 확인
CPU 바운드
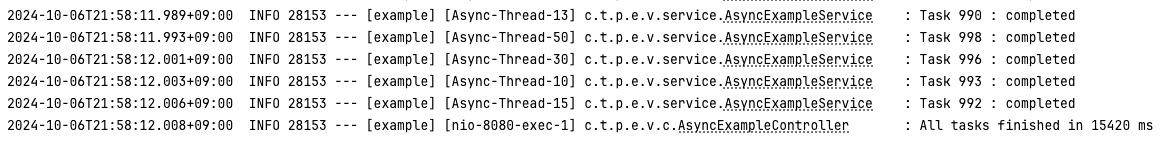
- platform thread
- 1회차 : 15,420 ms
- 2회차 : 17,280 ms
- 3회차 : 15,953 ms
- 평균 : 16,217 ms
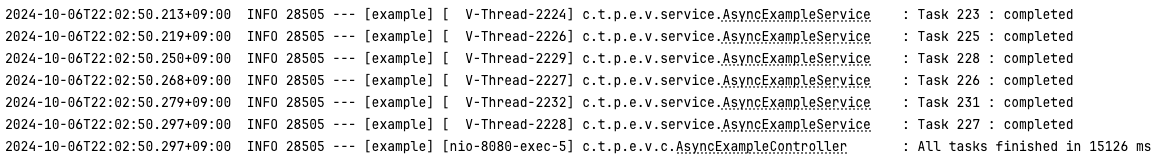
- virtual thread
- 1회차 : 15,126 ms
- 2회차 : 15,784 ms
- 3회차 : 12,557 ms
- 평균 : 14,489 ms
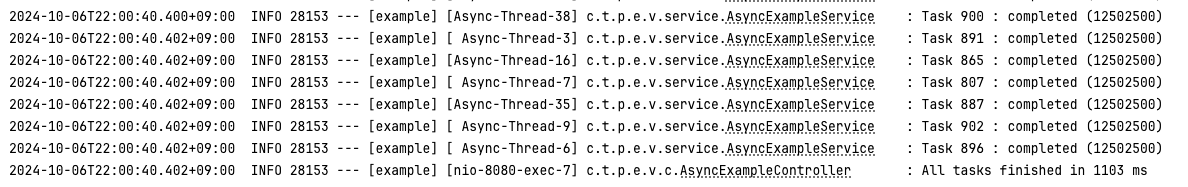
IO 바운드 (platform thread)
- platform thread
- 1회차 : 1,103 ms
- 2회차 : 1,557 ms
- 3회차 : 1,008 ms
- 평균 : 1,222 ms
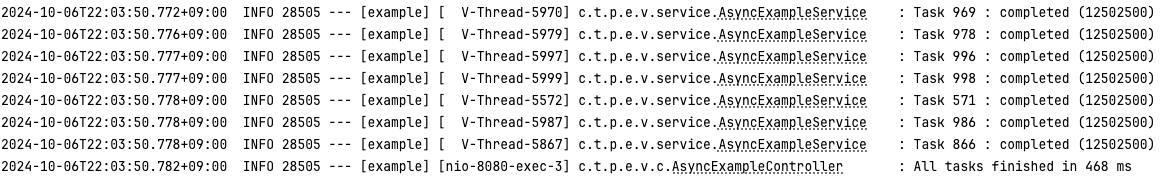
- virtual thread
- 1회차 : 468 ms
- 2회차 : 510 ms
- 3회차 : 726 ms
- 평균 : 568 ms
마무리
위 수행 결과들로 보았을때 우리가 알고있던대로 CPU bounded 작업의 경우 virtual thread 사용시 약간의 개선효과가 있어 보이기는 했지만 이는 오차범위 내에서 차이가 있었던것으로 보여지는 정도라서 사실상 효과가 그다지 나타나지 않았다고 해석 할 수 있을듯합니다. 하지만 역시나 IO bounded 작업의경우에는 성능이 2배 이상 개선되는 큰 효과를 보여주는것으로 확인되었습니다.
virtual thread 는 분명 고전적인 thread 처리 방식의 단점을 해결해줄 수 있는 신기술이 맞지만, 항상 모든 상황에서 기존 platform thread 에서 개선된 성능을 보여주는것은 아니기도 하고 특히나 pinning이 일어날 수 있는 작업 혹은 CPU 연산이 훨신 많이 필요한 작업등 virtual thread 사용시에는 동작 형태와 원리를 잘 파악하고 조심해서 사용해야 합니다.