java annotation processing
annotation processing이란, 말 그대로 annotation을 이용해서 작업을 처리하는 방법으로서, java5부터 지원됬습니다.
사실 실무개발에서 직접적으로 annotation processing을 직접 구현하는일은 많지 않기때문에 관심도가 많이 떨어지는 기능입니다. 하지만 많이들 사용하시는 Lombok이 annotation processing을 통해 필요한 코드들을 대신 만들어주고 있는데요, 이번포스팅에서 어떻게 동작하는지 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
annotation processing은 컴파일 단계에서 정의된 processor에 의해 바이트코드 혹은 java 파일등을 생성 할 수 있는 기능입니다. 따라서 런타임에서 추가적인 비용이 발생하지 않는다는 장점이 있습니다.
아래 CustomGetter를 만드는 예제 코드와 함께 자세히 알아보겠습니다.
예제에서는 한 프로젝트내에서 multi-module gradle을 통해 annotation 모듈과 app 모듈을 나누어 작성되어있습니다.
먼저, annotation 모듈 내에 dependency를 추가해줍니다.
// annotation module
// build.gradle
dependencies {
implementation 'com.squareup:javapoet:1.11.1'
implementation 'org.apache.commons:commons-lang3:3.9'
compileOnly 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc6'
annotationProcessor 'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc6'
}
'com.squareup:javapoet:1.11.1': java 파일 생성을 위한 dependency'com.google.auto.service:auto-service:1.0-rc6': processor 등록을 위한 dependency로서, 해당 코드 또한 annotationProcessing으로 동작하고 있습니다.
다음, CustomGetter annotation을 만들어 줍니다.
// annotation module
// CustomGetter.java
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE)
public @interface CustomGetter
{
}
@Target(ElementType.TYPE):class,interface,enumtype에 선언 될 수 있는 어노테이션 입니다.@Retention(RetentionPolicy.SOURCE): source 레벨에서 유지됩니다.
이제 핵심로직인 CustomGetter 어노테이션이 선언되었을때 동작할 프로세스를 구현해야 합니다. 간단하게 AbstractProcessor를 상속해 구현 할 수 있습니다.
// annotation module
// CustomGetterProcessor.java
@AutoService(Processor.class)
public class CustomGetterProcessor extends AbstractProcessor
{
@Override
public Set<String> getSupportedAnnotationTypes()
{
// 타겟 annotation class 정의
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
set.add(CustomGetter.class.getName());
return set;
}
@Override
public SourceVersion getSupportedSourceVersion()
{
// 타겟 source version 정의 (java 8, 11 ...)
return SourceVersion.latestSupported();
}
@Override
public boolean process(Set<? extends TypeElement> annotations, RoundEnvironment roundEnv)
{
Set<? extends Element> elemenets = roundEnv.getElementsAnnotatedWith(CustomGetter.class);
List<FieldSpec> fieldSpecList = new ArrayList<>();
List<MethodSpec> methodSpecList = new ArrayList<>();
for (Element element : elemenets)
{
if (element.getKind() != ElementKind.CLASS)
{
processingEnv.getMessager().printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, "CustomGetter have to annotated on class");
}
TypeElement typeElement = (TypeElement) element;
for (Element field : typeElement.getEnclosedElements())
{
if (field.getKind() == ElementKind.FIELD)
{
String fieldNm = field.getSimpleName().toString();
TypeName fieldTypeName = TypeName.get(field.asType());
FieldSpec fieldSpec = FieldSpec.builder(fieldTypeName, fieldNm)
.addModifiers(Modifier.PRIVATE)
.build();
fieldSpecList.add(fieldSpec);
String methodNm = String.format("get%s", StringUtils.capitalize(fieldNm));
String returnStatement = "return "+fieldNm;
MethodSpec methodSpec = MethodSpec.methodBuilder(methodNm)
.addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC)
.returns(fieldTypeName)
.addStatement(returnStatement)
.build();
methodSpecList.add(methodSpec);
}
}
ClassName className = ClassName.get(typeElement);
String getterClassName = String.format("%sGetter", className.simpleName());
TypeSpec getterClass = TypeSpec.classBuilder(getterClassName)
.addModifiers(Modifier.PUBLIC)
.addFields(fieldSpecList)
.addMethods(methodSpecList)
.build();
try
{
JavaFile.builder(className.packageName(), getterClass)
.build()
.writeTo(processingEnv.getFiler());
}
catch (IOException e)
{
processingEnv.getMessager().printMessage(Diagnostic.Kind.ERROR, "ERROR : " + e);
}
}
return true;
}
}
annotation 마다 원하는 로직에 따라 custom java 파일을 만들기위해 field, method, class를 정의해 컴파일 단계에서 소스를 생성 해 낼 수 있습니다.
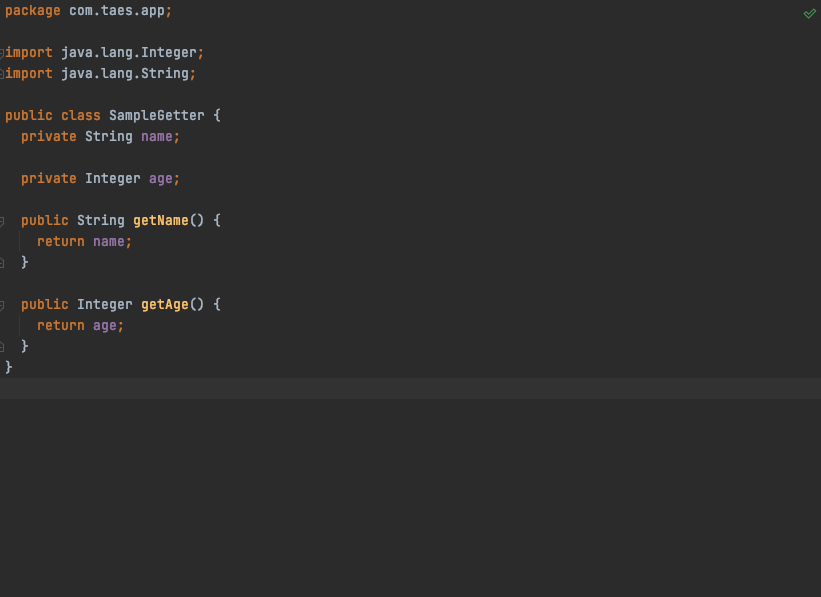
위 로직의경우 Lombok의 Getter를 모방한 클래스를 만들기위해, field를 그대로 가져오고, 필드마다 getMethod를 선언해 줌으로서 객체를 캡슐화한 클래스를 생성해주고 있습니다.
이제 위로직을 사용하기위해 'app 모듈'을 정의해 보겠습니다.
// app module
// build.gradle
dependencies {
compileOnly project(':annotation')
annotationProcessor project(':annotation')
}
// app module
// Main.java
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
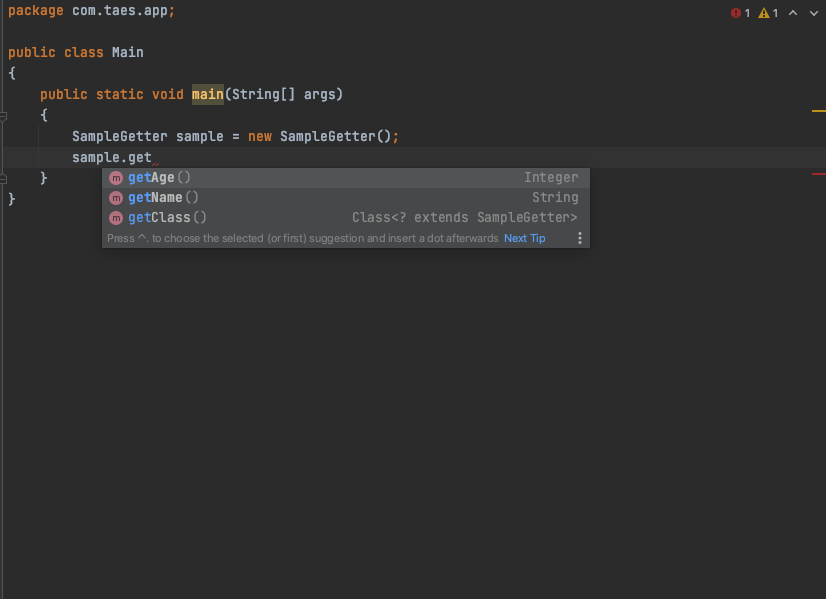
SampleGetter sample = new SampleGetter();
sample.getName();
sample.getAge();
}
}
// app module
// Sample.java
@CustomGetter
public class Sample
{
public String name;
public Integer age;
}
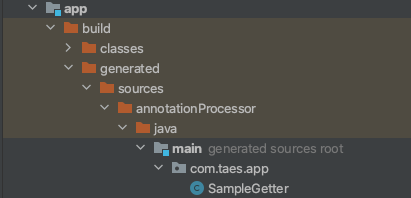
Sample 클래스에 위 annotation모듈에서 만들어준 @CustomGetter를 선언함으로서, build시 'build > generated > sources > annotationProcessor > java > main .. > SampleGetter' 라는 클래스가 annotation processing을 통해 만들어 지고 코드 레벨에서 사용 할 수있습니다.
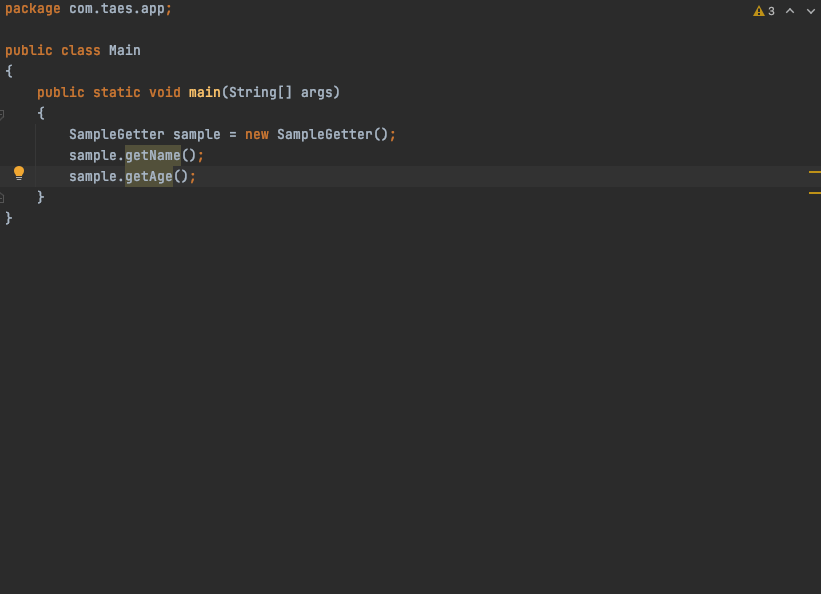
예제 코드 : https://github.com/taes-k/sample-annotation-processing
Lombok
위에서 예제 코드를 통해 annotation processing으로 CustomGetter를 만들어보았는데, 사실 조금 이상하다는것을 느끼셨을겁니다.
실제 Lombok의 경우 본래의 클래스에서 메서드, 생성자 등을 추가 해 주는데에 반해 위 예제에서는 새로운 클래스를 생성하고 있어 사용성이 많이 떨어집니다.
기본적으로 제공하는 annotation processing api는 기존에 존재하는 코드를 고치거나 수정할수는 없습니다.
Lombok 코드를 직접 열어보면 public api 를 사용하지 않고 별도의 handler를 통해 구현되어 있는것을 확인하실수 있습니다.
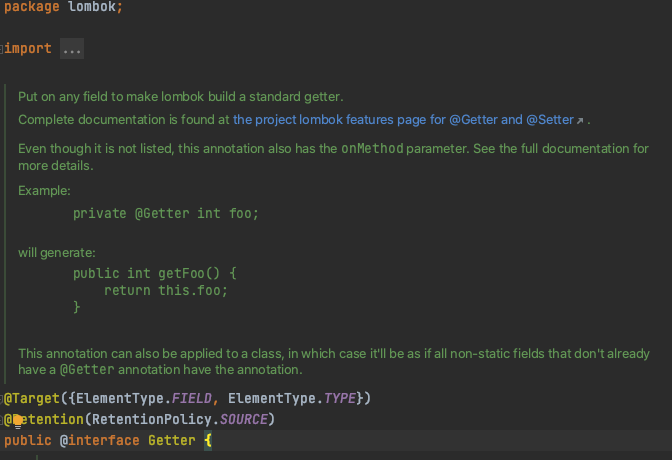
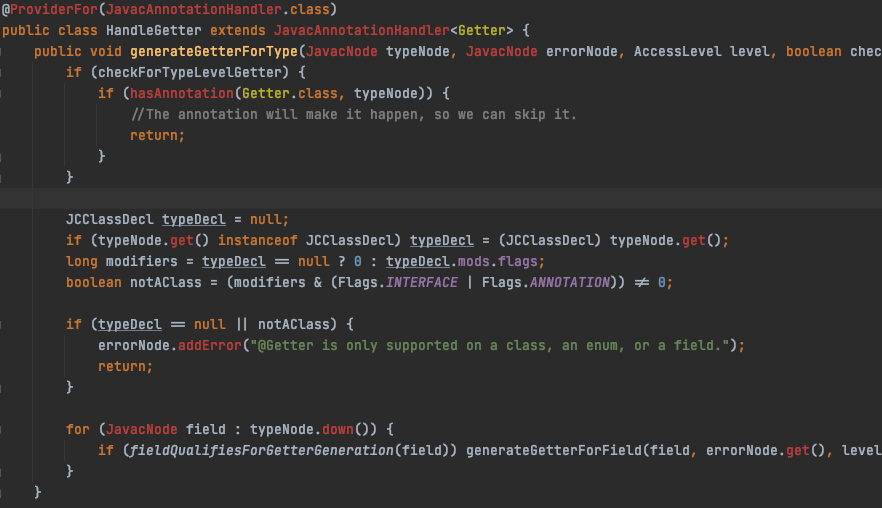
Lombok과 동일하게 동작하는 CustomLombok을 만들어보고자 하신다면, 아래 reference를 참조해주세요
- https://www.baeldung.com/lombok-custom-annotation
Reference
- https://www.baeldung.com/java-annotation-processing-builder