Spring AOP
객체 지향인 OOP 를 보완하기 위해 Spring 에서 제공하는 관점 지향의 AOP에 대해 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
OOP의 주된 모듈이 클래스이기 때문에 AOP는 유사한 목적을 갖는 클래스들을 관통할수 있도록 Aspect 단위로 모듈화를 합니다.
이를 위해 Proxy 를 사용하게 되는데 Spring에서는 기본적으로 두가지 방식을 통해 AOP제공합니다.
- JDK Proxy : Java 내부에 구현되어있는 Proxy
- CGLLIB Proxy : Open source로 구현되어있는 Proxy
proxy 메커니즘
먼저 Proxy 수행 메커니즘에 대해 알아보도록 합시다.
일반적으로 객체를 생성해 함수를 호출 할때는 아래와같은 코드로 이루어집니다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pojo pojo = new SimplePojo();
// this is a direct method call on the 'pojo' reference
pojo.foo();
}
}
public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
// this next method invocation is a direct call on the 'this' reference
this.bar();
}
public void bar() {
// some logic...
}
}
다이어그램으로 나타내면 아래와 같습니다.
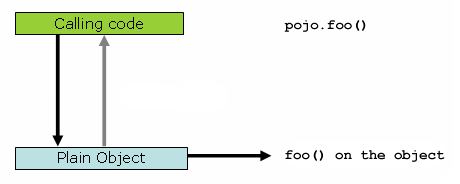
Proxy를 통해 함수를 호출할때는 다음과 같은 코드로 이루어집니다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());
factory.addInterface(Pojo.class);
factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());
Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo();
}
}
public class SimplePojo implements Pojo {
public void foo() {
// this next method invocation is a direct call on the 'this' reference
this.bar();
}
public void bar() {
// some logic...
}
}
다이어그램으로 나타내면 아래와 같습니다.
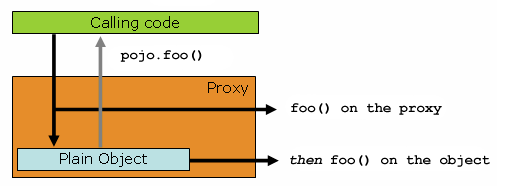
Proxy로 감싸진 객체를 선언함으로써 해당 객체의 함수 호출시 Proxy 내부의 로직에 따라 수행 후 결과를 얻게 될 것입니다.
Spring은 AOP가 필요한 환경에서 Bean 생성시 위와같은 Proxy Bean을 생성 해 줌으로써 method 수행시 부가기능을 주입해 수행 할 수 있도록 해 주는것입니다.
그렇다면 JDK dynmic proxy와 CGLIB proxy는 어떤 수행방식의 차이가 있을까요?
차이는 아래과 같습니다.
JDK dynamic proxy
- Reflection을 통해 동적으로 proxy 객체 생성
- interface를 기준으로 proxy 생성
JDK dynamic proxy는 아래와 같이 구현됩니다.
// DemoApplication.java
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
public class DemoApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SampleInterface sample = (SampleInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
SampleInterface.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[]{SampleInterface.class},
new SampleHandler());
sample.runSample();
}
}
// SampleInterface.java
public interface SampleInterface
{
String runSample();
}
// SampleImpl.java
@Slf4j
public class SampleImpl implements SampleInterface
{
public String runSample()
{
log.info("Run Sample");
return "returned sample";
}
}
// SampleHandler.java
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
@Slf4j
public class SampleHandler implements InvocationHandler
{
private final SampleInterface origin = new SampleImpl();
public void runBefore()
{
log.info("Run Before");
}
public void runAfter(Object result)
{
log.info("After RESULT : {}", result);
log.info("Run After");
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable
{
runBefore();
Object result = method.invoke(origin, args);
runAfter(result);
return null;
}
}
수행결과는 아래와 같습니다
21:07:20.608 [main] INFO com.example.transaction.demo.SampleHandler - Run Before
21:07:20.610 [main] INFO com.example.transaction.demo.SampleImpl - Run Sample
21:07:20.612 [main] INFO com.example.transaction.demo.SampleHandler - After RESULT : returned sample
21:07:20.613 [main] INFO com.example.transaction.demo.SampleHandler - Run After
위 코드를 보시면 아시다시피 JDK Dynamic proxy의 핵심은 InvocationHandler입니다.
InvocationHandler은 프록시로 선언한 method-call이 일어날때 지정한 핸들러를 통해 메서드가 수행되도록 조작해줍니다.
CGLIB (Code Generator Library) proxy
- 클래스 상속을 통해 proxy 객체 생성
- interface, class 기준으로 proxy 생성
- 타겟 클래스의 바이트코드를 조작하여 재정의 하기때문에 final 사용 불가
CGLIB proxy는 아래와같이 구현됩니다.
// DemoApplication.java
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer;
public class DemoApplication
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SampleImpl sample = (SampleImpl) Enhancer.create(SampleImpl.class, new SampleHandler());
sample.runSample();
}
}
// SampleImpl.java
@Slf4j
public class SampleImpl implements SampleInterface
{
public String runSample()
{
log.info("Run Sample");
return "returned sample";
}
}
// SampleHandler.java
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodInterceptor;
import org.springframework.cglib.proxy.MethodProxy;
@Slf4j
public class SampleHandler implements MethodInterceptor
{
public void runBefore()
{
log.info("Run Before");
}
public void runAfter(Object result)
{
log.info("After RESULT : {}", result);
log.info("Run After");
}
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable
{
runBefore();
Object result = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
runAfter(result);
return null;
}
}
수행결과는 아래와 같습니다
21:26:18.907 [main] INFO com.example.transaction.demo.SampleHandler - Run Before
21:26:18.915 [main] INFO com.example.transaction.demo.SampleImpl - Run Sample
21:26:18.916 [main] INFO com.example.transaction.demo.SampleHandler - After RESULT : returned sample
21:26:18.916 [main] INFO com.example.transaction.demo.SampleHandler - Run After
JDK dynamic proxy와 다른점은, Enhancer를 통해 interface가 아닌 구현체가 등록되어
MethodInterceptor에 의해 method-call이 일어날때 지정된 핸들러를 통해 메서드가 수행된다는 점 입니다.
두 방식의 구현방법 모두를 살펴보았는데요, 많은 실험으로 나온 결과로는 CGLIB proxy 방식이 일반적으로 성능이 좋게 측정됩니다. (해당 내용은 구글링을 통해 많은분들의 직접 실험한 결과를 확인하실수 있습니다.)
JDK dynamic Proxy vs CGLIB Proxy
그렇다면 둘중 어떤것을 사용해야 될까요? Spring document에서는 아래와 같이 정리하고 있습니다.
Spring AOP defaults to using standard JDK dynamic proxies for AOP proxies. This enables any interface (or set of interfaces) to be proxied.
Spring AOP can also use CGLIB proxies. This is necessary to proxy classes rather than interfaces. By default, CGLIB is used if a business object does not implement an interface. As it is good practice to program to interfaces rather than classes, business classes normally implement one or more business interfaces. It is possible to force the use of CGLIB, in those (hopefully rare) cases where you need to advise a method that is not declared on an interface or where you need to pass a proxied object to a method as a concrete type.
It is important to grasp the fact that Spring AOP is proxy-based. See Understanding AOP Proxies for a thorough examination of exactly what this implementation detail actually means.
(Spring doc - spring core - 4.5.3 AOP Proxies )
The ProxyFactoryBean now exhibits similar semantics with regard to auto-detecting interfaces as those of the TransactionProxyFactoryBean class.
If the class of a target object that is to be proxied (hereafter simply referred to as the target class) does not implement any interfaces, a CGLIB-based proxy is created. This is the easiest scenario, because JDK proxies are interface-based, and no interfaces means JDK proxying is not even possible. You can plug in the target bean and specify the list of interceptors by setting the interceptorNames property. Note that a CGLIB-based proxy is created even if the proxyTargetClass property of the ProxyFactoryBean has been set to false. (Doing so makes no sense and is best removed from the bean definition, because it is, at best, redundant, and, at worst confusing.)
If the target class implements one (or more) interfaces, the type of proxy that is created depends on the configuration of the ProxyFactoryBean.
If the proxyTargetClass property of the ProxyFactoryBean has been set to true, a CGLIB-based proxy is created. This makes sense and is in keeping with the principle of least surprise. Even if the proxyInterfaces property of the ProxyFactoryBean has been set to one or more fully qualified interface names, the fact that the proxyTargetClass property is set to true causes CGLIB-based proxying to be in effect.
If the proxyInterfaces property of the ProxyFactoryBean has been set to one or more fully qualified interface names, a JDK-based proxy is created. The created proxy implements all of the interfaces that were specified in the proxyInterfaces property. If the target class happens to implement a whole lot more interfaces than those specified in the proxyInterfaces property, that is all well and good, but those additional interfaces are not implemented by the returned proxy.
If the proxyInterfaces property of the ProxyFactoryBean has not been set, but the target class does implement one (or more) interfaces, the ProxyFactoryBean auto-detects the fact that the target class does actually implement at least one interface, and a JDK-based proxy is created. The interfaces that are actually proxied are all of the interfaces that the target class implements. In effect, this is the same as supplying a list of each and every interface that the target class implements to the proxyInterfaces property. However, it is significantly less work and less prone to typographical errors.
(Spring doc - spring core - 6.4.3 JDK- and CGLIB-based proxies )
관련해서 이야기하는 내용이 길지만 정리하면 다음과 같습니다
- Spring AOP 에서는 기본적으로 JDK dynamic proxy를 사용
- 인터페이스를 구현여부에 따라 선택적으로 사용
- proxy-target-class 설정에 따라 선택 가능
Spring framework 에서는 JDK dynamic proxy를 기본으로 사용합니다.
하지만 Spring Boot 프로젝트에서는 spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true 옵션을 default로 설정하여 기본적으로 CGLIB proxy를 사용하게 되어 있습니다.
이에 대해서 Spring boot에서 CGLIB를 채택하게된 이유를 아무래도 reflection 을 사용하는 JDK Dynamic proxy에 비해 unexpected cast exception이 발생 가능성이 적기때문이라고 합니다.
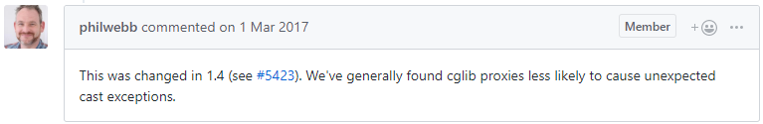
실제로 spring framework에서 proxy를 결정짓는 config 코드는 아래와 같습니다.
// TransactionAutoConfiguration.java
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnBean(TransactionManager.class)
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration.class)
public static class EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration {
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "false",
matchIfMissing = false)
public static class JdkDynamicAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@EnableTransactionManagement(proxyTargetClass = true)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "proxy-target-class", havingValue = "true",
matchIfMissing = true)
public static class CglibAutoProxyConfiguration {
}
}
Class에서 AOP를 사용할시 프로젝트 수행시 아래와같은 trace log를 확인 할 수 있습니다.
2021-02-07 19:13:14.322 TRACE 11350 --- [ main] o.s.b.a.condition.OnPropertyCondition : Condition OnPropertyCondition on org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.transaction.TransactionAutoConfiguration$EnableTransactionManagementConfiguration$CglibAutoProxyConfiguration matched due to @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true) matched
2021-02-07 20:59:07.499 TRACE 14724 --- [ main] o.s.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy : Creating CGLIB proxy: SingletonTargetSource for target object [com.example.transaction.demo.SampleService@4cc61eb1]
Interface에서 AOP를 사용하면 JDK dynamic proxy를 사용하는것을 확인 할 수 있습니다
2021-02-07 20:39:14.825 TRACE 14087 --- [ main] o.s.aop.framework.JdkDynamicAopProxy : Creating JDK dynamic proxy: SingletonTargetSource for target object [com.example.transaction.demo.SampleService@2d8f2f3a]
사실 기존에 CGLIB proxy가 기본 proxy로 사용되지 못했던 이유가 있습니다.
- 외부 라이브러리 (Java 기본 라이브러리가 아님)
- 디폴트 생성자가 필요함
- proxy 생성과정에서 생성자를 두번씩 호출
위의 문제점들이 현재는 Spring boot 가 업데이트 되는 과정에서 모두 해결되어 상황에 따라 두개의 proxy를 모두 사용 할 수 있게 되었습니다.
참고문서
- Spring doc : https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/core.htm
- Spring JDK Dynamic Proxy vs CGLIB 차이점 : https://tangoblog.tistory.com/8
- Spring AOP가 제공하는 두 가지 AOP Proxy : https://gmoon92.github.io/spring/aop/2019/04/20/jdk-dynamic-proxy-and-cglib.html