Call by Value, Call by Reference
Java Argument 전달방식에는 대부분 알고계시다시피 Call by value, Call by reference 두가지 방식이 있습니다.
이는 단어적의미로는 잘 와닿지는 않지만, 전문용어로 평가 전략(Evaluation Strategy)이라고 합니다.
Java의 Argument 전달방식을 알아보기전에 위 두가지 평가전략에대해서 간단하게 정의를 해보도록 하겠습니다.
Call by value
Call by value (also known as pass by value) is the most common evaluation strategy, used in languages as different as C and Scheme.
In call by value, the argument expression is evaluated, and the resulting value is bound to the corresponding variable in the function (frequently by copying the value into a new memory region)
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evaluation_strategy)
- 함수 호출시 argument 값을 복사한다.
Call by reference
Call by reference (or pass by reference) is an evaluation strategy where a function receives an implicit reference to a variable used as argument, rather than a copy of its value.
This typically means that the function can modify (i.e., assign to) the variable used as argument—something that will be seen by its caller.
(https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Evaluation_strategy)
- 함수 호출시 암시적 reference (메모리 주소값)를 넘겨준다.
Java 예제 코드
Java Argument 전달방식을 간단하게 알아보기 위한 예제 코드를 준비했습니다.
다음 코드의 출력결과는 어떻게 나올까요?
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
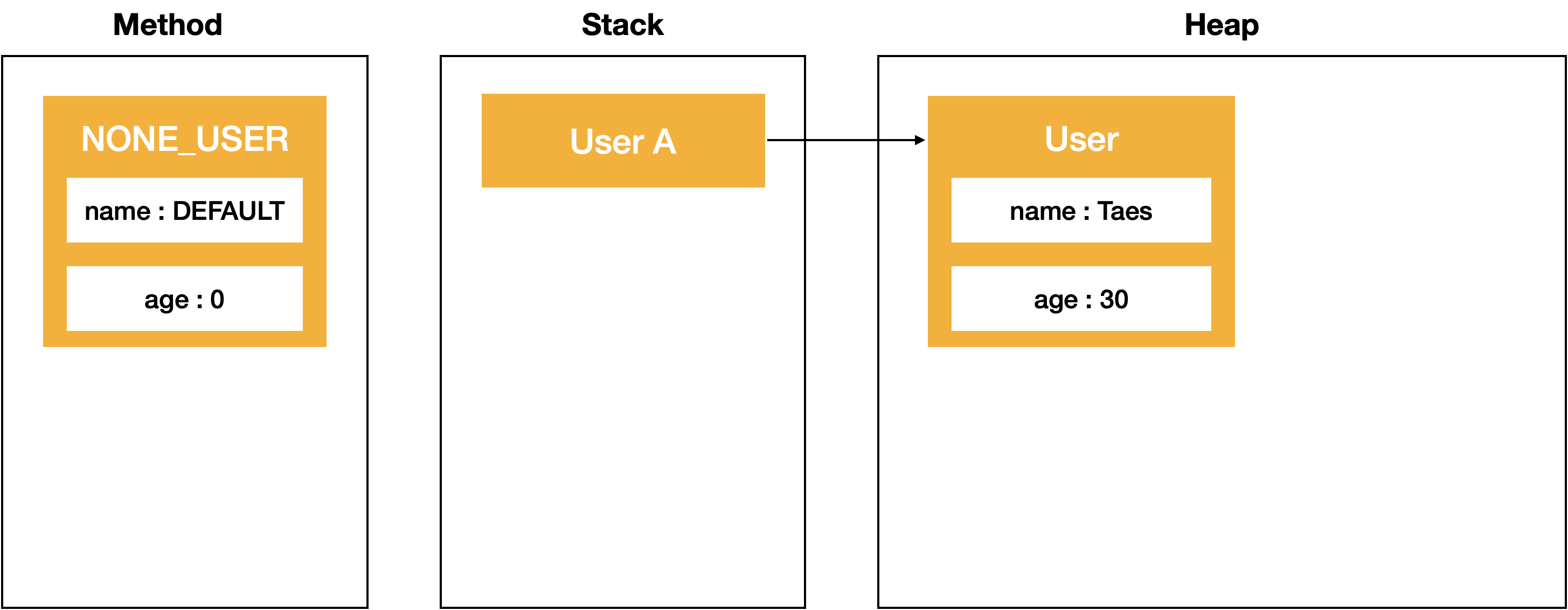
User userA = new User("Taes", 30);
changeUserName(userA);
System.out.println("1 : " + userA.name);
changeUser(userA);
System.out.println("2 : " + userA.name);
changeUserDefault(userA);
System.out.println("3 : " + userA.name);
}
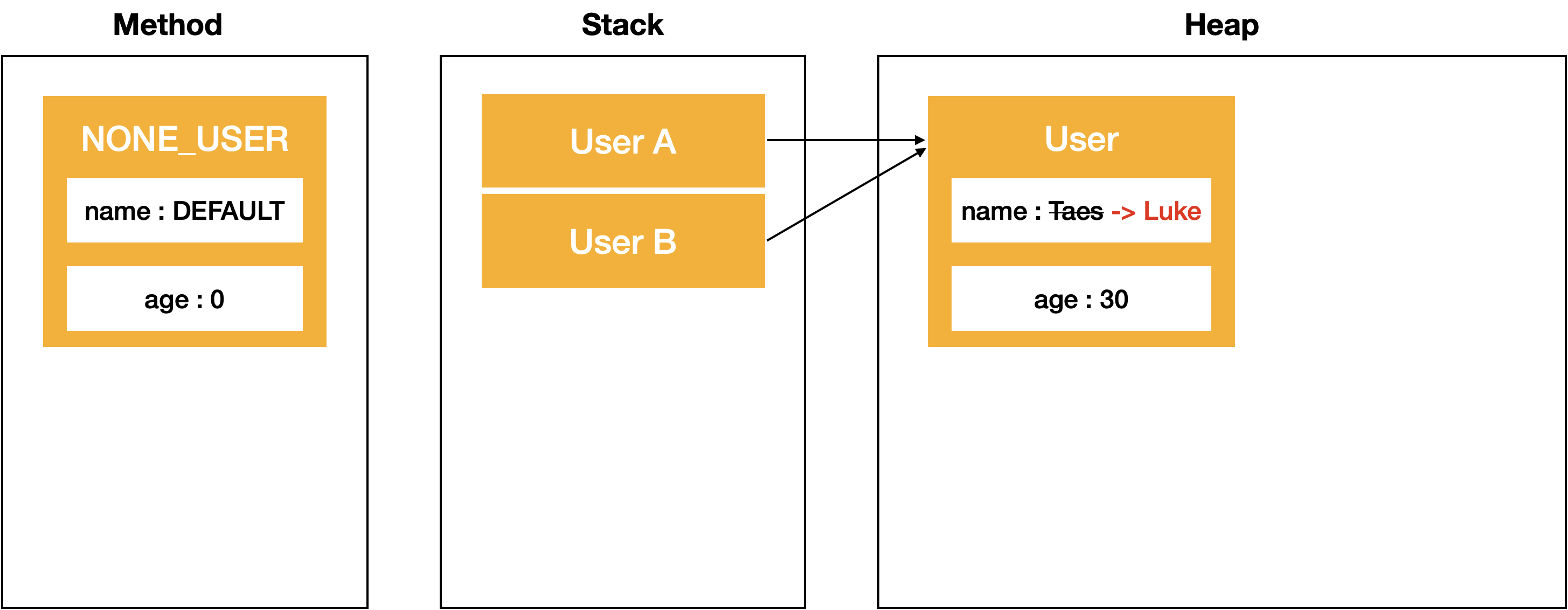
private static void changeUserName(User userB)
{
userB.name = "Luke";
}
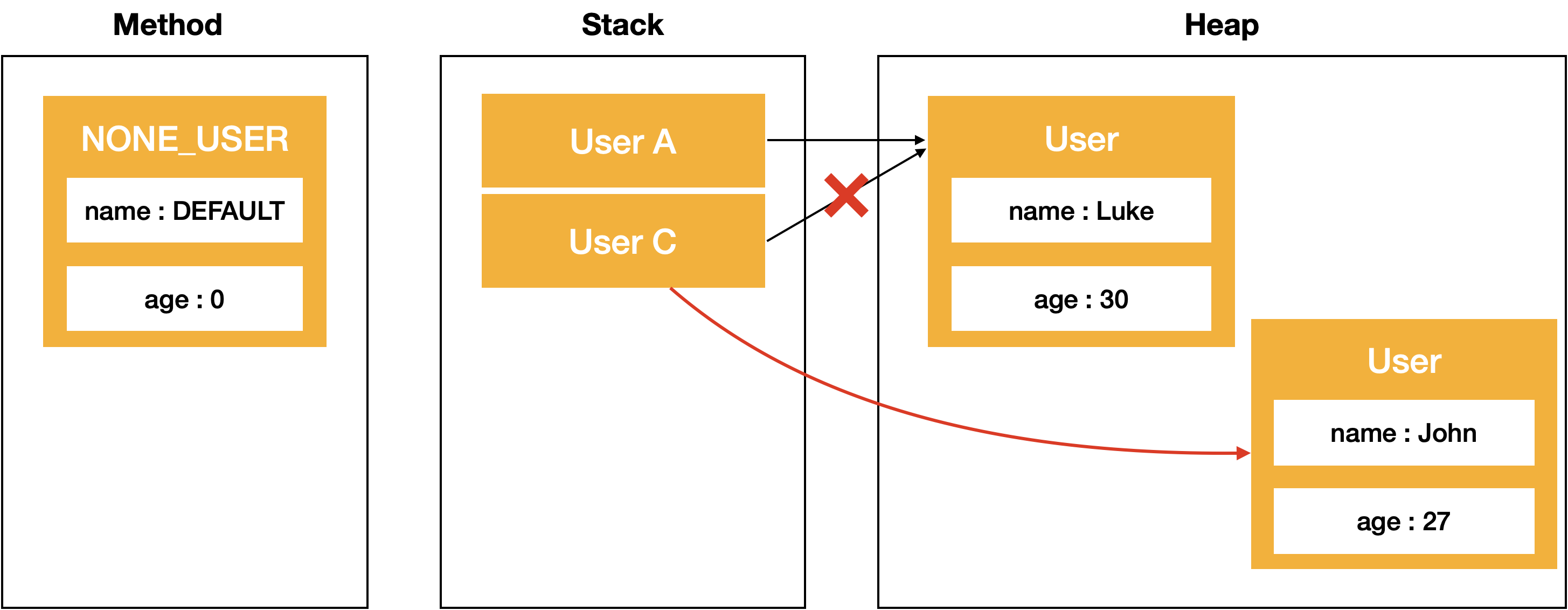
private static void changeUser(User userC)
{
userC = new User("John", 27);
}
private static void changeUserDefault(User userD)
{
userD = User.DEFAULT_USER;
}
}
class User {
public String name;
public int age;
public static User DEFAULT_USER = new User("DEFAULT", 0);
public User(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
jvm stack & heap memory
먼저, 결과부터 알려드리자면, 아래와 같습니다.
1 : Luke
2 : Luke
3 : Luke
아마, java 에서는 객체를 넘길때는 Call by reference로 동작하기 때문에 생각하셨던 결과가 아니라고 예상하셨던분이 계실거라 생각합니다.
이러한 결과가 나온 이유를 명확하게 하기 위해, 실제 메모리상에서 데이터가 어떻게 저장되고 있는지 아는것이 중요합니다.
아시다시피 jvm은 크게 method, stack, heap 3가지 영역으로 구성됩니다.
그 중 stack 메모리 영역에 저장되는 데이터는 아래와 같습니다.
- 지역변수 (
reference 변수) - primitive type 데이터
heap 메모리 영역에 저장되는 데이터는 아래와 같습니다.
- 인스턴스 (
object, 객체)
위 내용을 기억 해 주시고, 그림을 통해 위 예제코드가 메모리상에 어떻게 저장되는지 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
public static class User
{
public String name;
public int age;
public static User DEFAULT_USER = new User("DEFAULT", 0);
public User(String name, int age)
{
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}
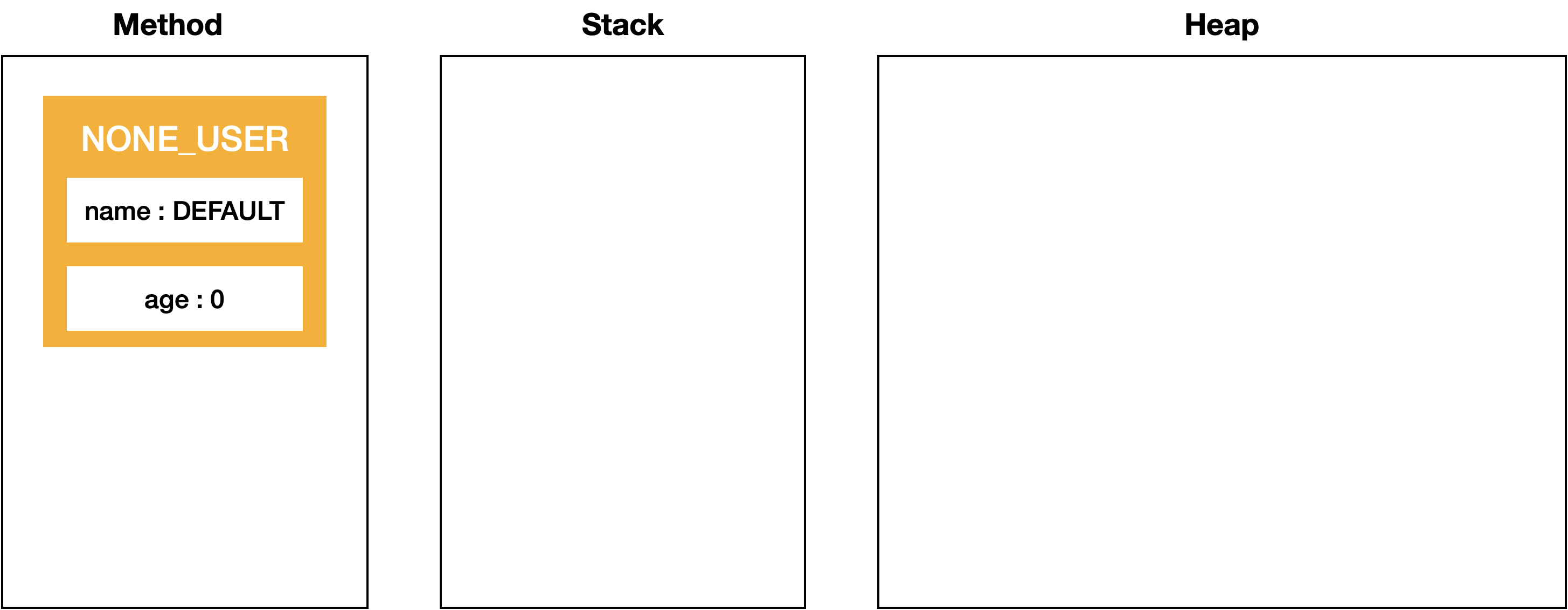
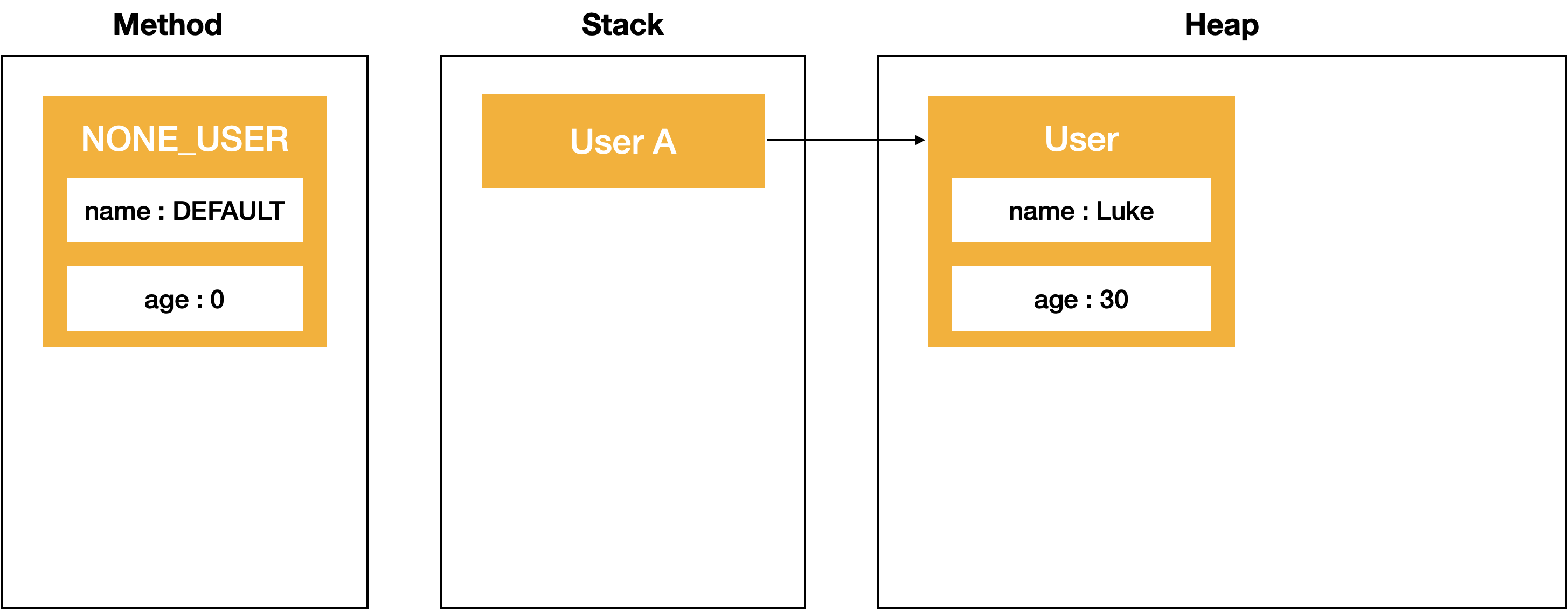
User userA = new User("Taes", 30);
private static void changeUserName(User userB)
{
userB.name = "Luke";
}
private static void changeUser(User userC)
{
userC = new User("John", 27);
}
private static void changeUserDefault(User userD)
{
userD = User.DEFAULT_USER;
}
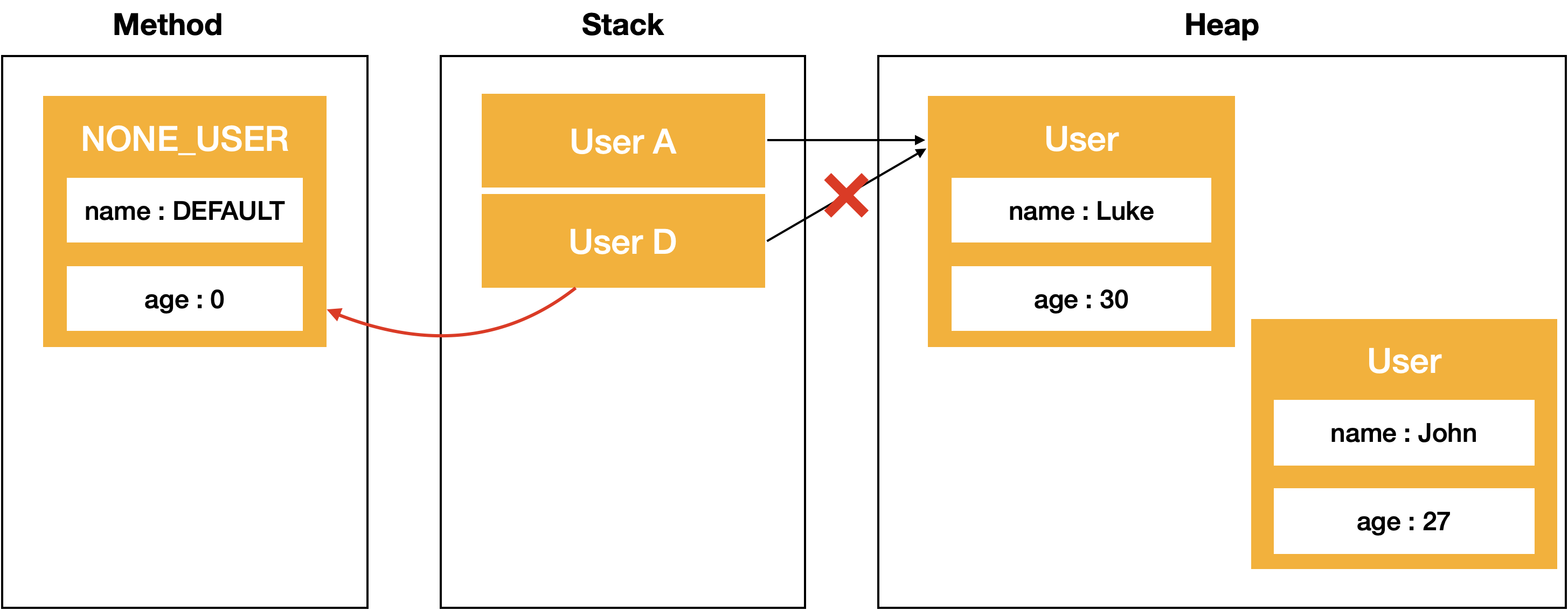
함수 호출이 모두 끝나고 난 후에는 최종적으로 아래와같은 메모리가 확인 될 것 입니다.
Java는 Call by value
예제 코드에서 changeUserName(User userB) 수행을 통해 userA의 name필드가 ‘Taes’ 에서 ‘Luke’로 변경된 것을 확인하였습니다.
이 결과만 보면, 호출 함수 내에서도 전달한 참조 객체가 그대로 사용전달되어 사용되어진 것이 확인 되기 때문에 Call-by-reference로 동작했다고 생각 할 수도 있겠습니다.
하지만 아래 changeUser(User userC)의 수행결과와 자바의 메모리 할당 과정을 보면 함수 호출시 userC라는 레퍼런스 변수가 복사되어 사용되고, 새로운 인스턴스 할당시에는 해당 레퍼런스 객체의 참조값만 변경되기 때문에 본래의 ‘Luke’ 객체는 아무 영향을 받지 않는다는것을 확인하실수 있습니다.
즉, Java의 Argument 전달방식은 참조값을 담은 레퍼런스 변수를 복사 하는 방식, 'Call-by-value'로 수행되는 것 입니다.