1.3 Spring Aspect (AOP)
이전 챕터에서 알아본 Spring의 IoC/DI와 더불어 Spring의 핵심 3요소중 하나인 AOP에 대해서 알아보려고 합니다. Aspect Oriented Programing 직역하면 ‘관점 지향 프로그래밍’이라고 하면 사실 어떤 프로그래밍 방식을 뜻하는지 알수가 없습니다. Spring에서 말하는 Aspect란 무엇인지 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
Contents List
1.3.1) Aspect Oriented Programming
AOP란?
먼저 스프링에서 말하는 AOP에 대해 정확히 알아보기 위해 스프링 공식 문서를 확인해보도록 하겠습니다.
Aspect-oriented Programming (AOP) complements Object-oriented Programming (OOP) by providing another way of thinking about program structure. The key unit of modularity in OOP is the class, whereas in AOP the unit of modularity is the aspect. Aspects enable the modularization of concerns (such as transaction management) that cut across multiple types and objects. (Such concerns are often termed “crosscutting” concerns in AOP literature.)
One of the key components of Spring is the AOP framework. While the Spring IoC container does not depend on AOP (meaning you do not need to use AOP if you don’t want to), AOP complements Spring IoC to provide a very capable middleware solution.
- AOP란 OOP를 보완하는 구조.
- OOP에서는 클래스단위로 모듈화를 했다면 AOP에서는 ‘관점’으로 모듈화를 하는 구조.
- ‘관점’은 type과 object와는 무관하게 ‘관심사항’으로 모듈화를 가능하게 한다.
- 스프링에서 AOP는 스프링 IoC를 보완하며 뛰어난 미들웨어 솔루션을 제공한다.
즉, AOP는 클래스와 관계없이 여러 객체를 관통하는 ‘공통 관심 사항’들에 따라서 묶어서 관리 해 줄수있는 구조라고 할수 있을것 같습니다.
결국 반복적인 코드들을 사용 목적(공통 관심 사항)에 따라서 공통된 통합 위임 코드를 작성하여 운영 및 관리할수 있게끔 하려는 목적에 있습니다.
AOP 개념과 용어
AOP가 어떻게 사용되는지 알아보기 전에 사용되는 용어들을 먼저 정리해보도록 하겠습니다.
| 용어 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| Aspect | 여러 객체를 관통하는 ‘공통 관심 사항’을 구현한것을 의미합니다. Spring 에서는 설정을 통해 일반 클래스에 넣는 방식(schema-based approach) 혹은 어노테이션을 활용한 방식으로 클래스에 aspect를 줄수 있습니다. |
| Join point | 특정 작업이 시작되는 시점을 나타내는 포인트로, 메서드 호출이나 예외발생 등의 시점들을 의미합니다. |
| Advice | 특정 join point에서 실행되는 action을 뜻하며, 실행 시점에따라 ‘around’, ‘before’, ‘after’의 타입들을 가지고 있습니다. |
| Pointcut | Join point의 부분집합으로써, 실제 Advice가 실행되는 Join point들의 집합을 의미합니다. |
| Target object | advise가 적용되어질 타깃 객체를 의미합니다. |
| AOP proxy | Aspect를 구현하기위해 AOP 프레임워크에서 만들어낸 객체를 의미합니다. |
| Introduction | proxy 객체에 메소드나 필드를 추가한것을 의미합니다. |
| weaving | Aspect를 Target object에 적용하는것. 컴파일시, 로드타입시, 런타임시 적용시킬수 있으나 Spring에서는 런타임때 적용시킵니다. |
1.3.2) Spring AOP Mechanisms>
AOP Proxy Factory
위에서 AOP와, AOP에서 사용되는 용어를 알아보았으니 이제 실제로 Spring에서는 어떠한 방식으로 AOP를 구현하고 있는지 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
스프링 AOP는 Proxy 기반으로 작동됩니다. ‘Proxy 기반으로 작동된다’는 의미를 다음 예제를 통해 알아보도록 하겠습니다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Pojo pojo = new SimplePojo();
// this is a direct method call on the 'pojo' reference
pojo.foo();
}
}
일반적인 방식으로 객체를 선언하여 메소드를 호출할때의 모식도는 다음과 같습니다.
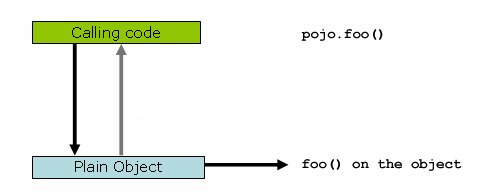
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory(new SimplePojo());
factory.addInterface(Pojo.class);
factory.addAdvice(new RetryAdvice());
factory.setExposeProxy(true);
Pojo pojo = (Pojo) factory.getProxy();
// this is a method call on the proxy!
pojo.foo();
}
}
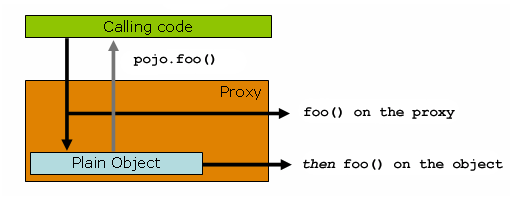
여기서 중요한점은, 클라이언트는 결국 pojo.foo 타깃을 요청하지만 DI를 통해 프록시가 주입되어 메소드 호출이 프록시내에서 일어나면서 프록시는 모든 메서드 call 에 대한 interceptor들을 위임받아 설정한 Advice를 실행 시킬수 있게 됩니다. 이것이 스프링 AOP에서 사용되는 ProxyFactory 패턴 입니다.
Spring AOP 적용
실제로 Spring AOP를 어떻게 적용시키는지 예제를 통해 알아보도록 하겠습니다. 다음 예제는 성능을 진단하는 프로파일링을 위해 시간을 체크하는 Aspect 예제입니다.
package foo;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.util.StopWatch;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;
@Aspect
public class ProfilingAspect {
@Around("methodsToBeProfiled()")
public Object profile(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
StopWatch sw = new StopWatch(getClass().getSimpleName());
try {
sw.start(pjp.getSignature().getName());
return pjp.proceed();
} finally {
sw.stop();
System.out.println(sw.prettyPrint());
}
}
@Pointcut("execution(public * foo..*.*(..))")
public void methodsToBeProfiled(){}
}
위와 같이 pointcut과 advice 를 선언하여 Aspect 를 구성했습니다. Pointcut에서 사용한 execution 명시자의 경우 표현식이 다음과 같습니다. execution(수식어패턴? 리턴타입패턴 패키지패턴?이름패턴(파라미터패턴) 따라서 위 예제의 경우 foo 패키지내 모든 메서드들에대해 profile advice가 동작하여 시간을 체크하게 될것입니다.
실제 프로젝트에서의 AOP 사용
- 로깅
@Aspect public class LoggingAspect { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(MessageAdvice.class); @Before("methodsToBeLogging()") public Object profile(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable { logger.info("메서드 :"+jp.getSignature().getName()); logger.info("매개변수 :"+Arrays.toString(jp.getArgs()); } @Pointcut("execution(public * foo..*.*(..))") public void methodsToBeLogging(){} } - 에러처리
@Aspect public class ErrorHandlingAspect { @Around("methodsToBeErrorHandling()") public Object profile(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable { try { result = jp.proceed(); } catch (Throwable e) { logger.error("[" + jp.toString() + "]*" + e); //errorHandling ... } } @Pointcut("execution(public * foo..*.*(..))") public void methodsToBeErrorHandling(){} }
마무리
Spring AOP가 어떻게 실행되는 알아보았는데, 결국 코드는 꽤나 단순하게 사용이 가능했습니다. 몇가지 설정만 해주면 스프링에서 AOP를 위한 프록시팩토리를 자동으로 생성하여 본래의 코드에 변화없이 Aspect를 실행 시켜 줄 수 있습니다. 이것이 스프링이 가지고 있는 AOP 프레임워크이며 IoC컨테이너와 보완적으로 AOP를 사용할수 있습니다.
참조 문서
Spring 5.1.6 release docs
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/core.html#aop